A Deep Dive into Advanced CFD Modeling in DVS Heat Transfer Systems
A Comprehensive Guide to Selecting the Right Heat Transfer Equipments for Your Requirements
Picking the suitable Heat transfer system is essential for functional effectiveness. Different systems satisfy different needs, affected by aspects such as temperature level variety and fluid kind. Comprehending the concepts behind Heat transfer, such as convection, conduction, and radiation, is critical. Furthermore, evaluating energy sources and maintenance techniques can affect long-term performance. A closer exam of these considerations exposes exactly how to customize a system to details demands. What should one prioritize in this complex decision-making procedure?
Understanding Heat Transfer: Key Ideas and Concepts
Although Heat transfer may feel like a simple principle, it encompasses an array of principles that are essential for efficient system design. Understanding these principles is crucial for engineers and designers that intend to maximize thermal efficiency in different applications. Transmission, for instance, involves the transfer of Heat via solid materials, while convection refers to the movement of Heat within liquids. Radiation, another crucial concept, explains exactly how Heat can be moved via electro-magnetic waves. Each of these devices plays a crucial role in determining how energy relocates within a system. By extensively understanding these concepts, experts can make enlightened decisions, ensuring that Heat transfer systems operate effectively and fulfill the particular needs of their applications
Kinds Of Heat Transfer Equipments: An Overview
Understanding the concepts of Heat transfer lays the foundation for exploring the different kinds of Heat transfer systems available. Heat transfer systems can be categorized mostly into three kinds: conduction, radiation, and convection. Conduction entails Heat transfer through solid materials, relying upon straight call between particles. Convection, on the other hand, takes place in liquids (gases and liquids) where the movement of the liquid itself helps with Heat transfer. Radiation entails the transfer of Heat with electro-magnetic waves and does not require a medium, permitting it to take place in a vacuum cleaner. Each kind of system has distinct features and applications, making it essential for people and companies to thoroughly assess their specific needs when choosing one of the most ideal Heat transfer service.
Applications of Heat Transfer Solutions in Different Industries
Heat transfer systems play a vital function across various markets, impacting efficiency and product top quality. In commercial manufacturing procedures, they help with specific temperature control, while in food and drink processing, they assure security and preservation. In addition, cooling and heating and climate control systems depend greatly on reliable Heat transfer to maintain comfy settings.
Industrial Production Processes

Countless commercial production processes rely heavily on efficient Heat transfer systems to make best use of performance and improve product quality. In industries such as metalworking, Heat exchangers play an essential role in maintaining suitable temperatures during welding, casting, and forging. These systems guarantee consistent Heat distribution, which is vital for accomplishing preferred material properties. In a similar way, in the chemical manufacturing sector, Heat transfer systems facilitate specific temperature level control throughout reactions, impacting yield and safety. In fabric manufacturing, reliable Heat administration is essential for dyeing and ending up procedures, influencing color uniformity and material high quality. By choosing suitable Heat transfer modern technologies, makers can boost energy performance and minimize operational costs, inevitably causing a more sustainable and affordable manufacturing atmosphere.
Food and Beverage Handling
Reliable Heat transfer systems are equally vital in the food and beverage handling sector, where keeping perfect temperatures is essential for food security and quality. These systems play an essential function in processes such as sanitation, pasteurization, and food preparation, making sure that products are safe for usage and retain their dietary value. Heat exchangers, as an example, successfully transfer Heat in between fluids, optimizing power use while minimizing temperature variations. Additionally, refrigeration systems are basic for preserving disposable things and prolonging rack life. The choice of Heat transfer technology straight impacts operational performance and item integrity, making it critical for food and beverage suppliers to choose the proper systems tailored to their certain processing demands. This cautious selection eventually adds to customer satisfaction and food safety.
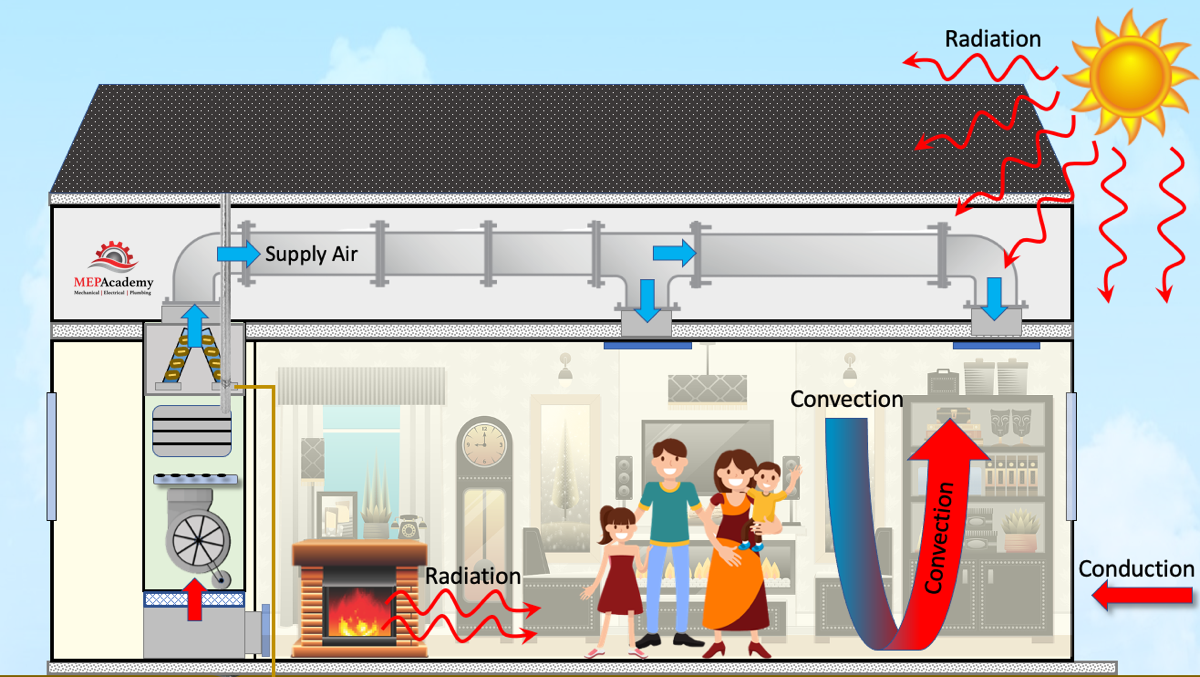
HVAC and Environment Control
While numerous sectors depend on Heat transfer systems for effectiveness, A/C (Home Heating, Ventilation, and A/c) plays an important role in preserving interior climate control throughout different settings. These systems utilize Heat transfer principles to manage humidity, temperature level, and air quality, making sure convenience and safety in domestic, industrial, and industrial atmospheres. Properly created heating and cooling systems enhance energy effectiveness, lower wikipedia reference operational costs, and minimize environmental effect. In commercial buildings, as an example, effective climate control adds to employee efficiency and customer fulfillment. In industrial applications, heating and cooling systems aid maintain excellent conditions for equipment procedure and product conservation. Picking the best Heat transfer system is vital for conference particular environment control needs and accomplishing overall system performance.
Examining Power Resources for Heat Transfer Solutions
In assessing energy resources for Heat transfer systems, a comparison of renewable energy options and fossil gas factors to consider is important. Eco-friendly resources, such as solar and wind, deal lasting choices that can lower ecological impact. On the other hand, nonrenewable fuel sources stay common due to their well established infrastructure and power density, prompting a mindful analysis of both choices.
Renewable Resource Options

Fossil Fuel Factors To Consider
Assessing fossil gas considerations is important for the effectiveness and sustainability of Heat transfer systems. Fossil gas, such as gas, oil, and coal, are typical energy sources that offer substantial Heat outcome, making them preferred choices for domestic and industrial applications. Nevertheless, their ecological influence, consisting of greenhouse gas discharges and source depletion, increases worries. When picking a warm transfer system, it is essential to analyze the schedule, cost, and governing elements related to these fuels. In addition, the efficiency of nonrenewable fuel source systems need to be thought about, as higher performance can mitigate some environmental drawbacks. Inevitably, a well balanced method weighing efficiency and important site sustainability can assist decision-makers toward the most ideal Heat transfer solution for their particular needs.
Elements to Take Into Consideration When Choosing a Heat Transfer System
Selecting an appropriate Heat transfer system calls for careful factor to consider of various variables that can significantly affect effectiveness and efficiency. One vital aspect is the operating temperature range, which determines the materials and style ideal for the application. In addition, the sort of liquid made use of in the system-- whether gas or fluid-- affects Heat transfer performance and compatibility. The system's size and capability should straighten with the particular demands of the procedure to avoid inefficiencies. Energy resource schedule is also essential, influencing operating expense and sustainability. The installment environment, including room restraints and ease of access for upkeep, plays a significant role in system selection. Finally, regulative compliance and safety and security standards need to be thought about to assure the system satisfies all lawful requirements.
Maintenance and Efficiency Optimization for Heat Transfer Equipments
Preserving Heat transfer systems is necessary for making certain maximum efficiency and longevity. Normal maintenance tasks, such as cleansing Heat exchangers and examining insulation, aid avoid performance losses because of fouling and thermal linking. In addition, monitoring system criteria, consisting of stress and temperature level, permits very early discovery of anomalies, reducing downtime and expensive fixings. Applying a preventative upkeep schedule can maximize performance and extend the life-span of components. Additionally, updating to advanced control systems can enhance functional effectiveness by changing to varying lots and problems. By prioritizing maintenance and performance optimization, drivers can achieve reduced power consumption, lower functional prices, and boosted overall system reliability, eventually bring about better resource use and an extra lasting procedure.
Future Patterns in Heat Transfer Technologies
As sectors increasingly focus on sustainability and power performance, future patterns in Heat transfer modern technologies are readied to undergo significant makeovers. Developments such as innovative materials, including carbon nanotubes and nanofluids, assure enhanced thermal conductivity and efficiency. Furthermore, the assimilation of eco-friendly power resources into Heat transfer systems is gaining momentum, advertising green remedies. Smart innovations, including IoT sensors, are anticipated to change tracking and control, enabling real-time information evaluation for enhanced performance. Furthermore, the advancement of small and modular systems will certainly promote less complicated setup and upkeep, accommodating diverse applications. These innovations suggest a shift towards even more sustainable, reliable, and adaptable Heat transfer remedies, aligning with international energy goals and ecological standards.
Regularly Asked Questions
What Are the Ecological Impacts of Heat Transfer Solutions?
The ecological impacts of Heat transfer systems can consist of greenhouse gas emissions, power intake, and prospective thermal pollution. In addition, inappropriate disposal of inefficiencies and products can contribute to resource exhaustion and ecological community interruption.
Just how Do I Compute the Cost-Effectiveness of a Heat Transfer System?
To determine the cost-effectiveness of a warmth transfer system, one must evaluate preliminary prices, operational expenditures, upkeep requirements, and energy effectiveness, contrasting these factors against the expected life expectancy and performance of the system.
Can Heat Transfer Systems Be Utilized in Residential Settings?
Heat transfer systems can indeed be utilized in property setups. They give efficient home heating and cooling remedies, making homes much more comfortable while potentially lowering energy prices. Their flexibility enables for different applications in property atmospheres.
What Security Laws Put On Heat Transfer Equipments?
Safety and security guidelines for Heat transfer systems commonly consist of standards on maintenance, procedure, and installation. Compliance with this hyperlink local building regulations, manufacturer requirements, and sector standards is important to assure reliable and secure system efficiency in different applications.
Exactly How Do Different Products Affect Heat Transfer Performance?
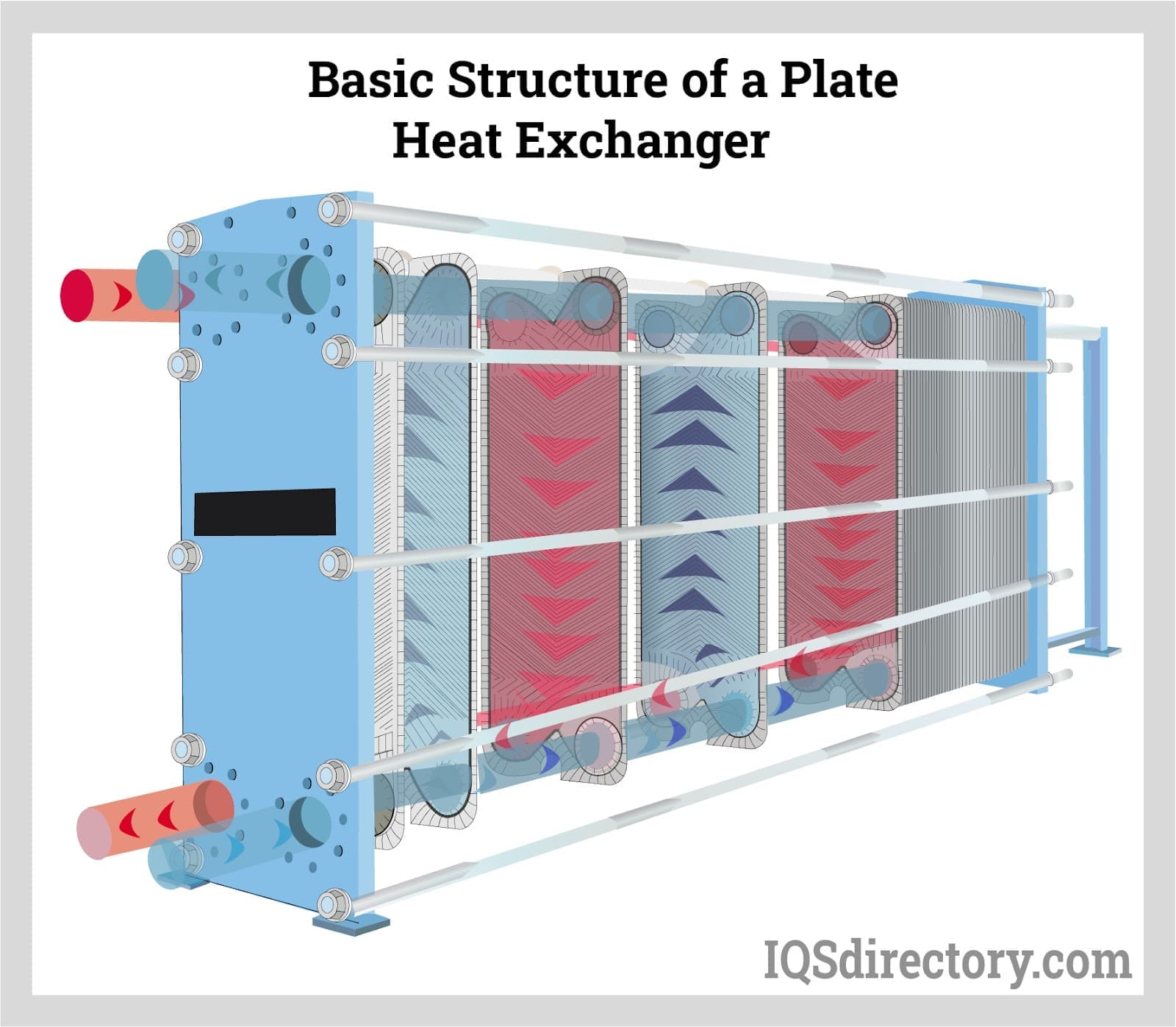
Transmission, for instance, involves the transfer of Heat through solid materials, while convection refers to the movement of Heat within fluids. Understanding the principles of Heat transfer lays the foundation for discovering the numerous kinds of Heat transfer systems readily available. Heat exchangers, for instance, efficiently transfer Heat between liquids, optimizing power usage while lessening temperature fluctuations. In evaluating energy sources for Heat transfer systems, a contrast of sustainable energy options and fossil gas considerations is vital. Steels, such as copper and light weight aluminum, conduct Heat efficiently, whereas insulators like rubber and glass slow down Heat circulation.